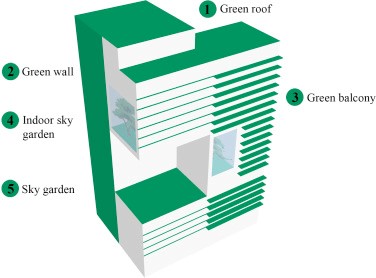
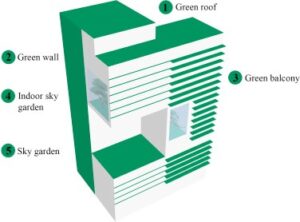
Introduction: The scarcity of energy and the deterioration of the environment have emerged as two of the most serious issues facing people today as a result of the economy and society’s rapid development. The building industry is today the largest user of global energy resources, as well as a leading source of environmental pollution. It also consumes a variety of resources, including ores, wood, and other resources. Therefore, in order to improve the current situation of high resource consumption and high environmental pollution, the building industry immediately needs to understand and design the sustainable development model. Green building is the practice of designing buildings and adopting resource- and ecofriendly solutions. It conserves natural resources, makes better use of energy, consumes less water, and produces less waste. It provides occupants healthier environments compared to a conventional building. Green buildings protect valuable natural resources and raise our standard of living. Green building, is the practice of maximizing resource conservation, such as energy, land, water, materials, and many others; protecting the environment and reducing pollution; providing a healthy, useful, and efficient living space for people; and coexisting peacefully with nature throughout building’s life cycle, as defined by the Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development in 2006. Buildings use around 15% of the world’s fresh water resources, 40% of the world’s energy, and emit about 30% of the world’s greenhouse gas emissions, including the effects of construction, operations, and deconstruction. It’s critical to reduce other harmful environmental effects and avert the worst effects of global climate change in order to discuss the effects of buildings on the environment. The world’s building industry has been moving toward green building as it has been more and more well-known and widely used in a growing number of countries. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) defines a green building as one that is resource- and environmentally-conscious throughout every stage of its existence, from planning to demolition.
Goals of Green Building:
- Reducing impacts on the Earth from constructing buildings and their materials.
- Reducing impacts which arise during occupancy.
- Reducing the impact of the structure at the end of its life.
- Creating a more desirable human experience.
Benefits Of Green Building:
An environmental solution: – Green buildings reduce waste, water, energy, and carbon emissions. The Department of Energy were reviewed 22 LEED-certified buildings managed by the General Services Administration and they found LEED-certified buildings have CO2 emissions which have been 34% lower, used 25% less energy and 11% less water, and prevented more than 80 million tons of waste from landfills.
Keep It Clean: Protecting Our Ecosystem: Since many years, there has been an increase in concern for global warming. In additional to being more environmentally friendly and healthier for its occupants, sustainable design also helps the planet. Green building is effectively help to maintain and promote a healthier environment by reducing human dependency on non-renewable resources (like coal and oil).
Prioritizing people’s health and well-being: Green building has a positive impact on public health. By Improving indoor air quality can reduce absenteeism and work hours affected by asthma, respiratory allergies, depression and stress as well as self-reported increases in productivity. Employees in LEED green buildings feeling happier, healthier, and more productive, according to USGBC’s research.
Enhances Indoor Environment Quality: The quality of the indoor environment is affected by the conditions inside a building and how those conditions affect its occupants. Lighting, ergonomics, climatic conditions, and air quality are some of these elements. A good indoor environment quality is one that protects the occupants’ health, reduces their stress levels, and enhances their quality of life. Green buildings do this by using materials that are less likely to emit harmful substances into the environment and by installing operable windows that let in as much natural light as possible.
Emerging Trends in Green Building Construction:
Low-income housing: The goal of the low-cost housing project is to support the building of each home. Due to these financial restrictions, the apartments normally only come with two plug outlets, two light units, and a small pre-paid electricity unit, but they do establish a variety of energy-saving strategies that can be adopted into low-income housing. These steps include adding insulation to the ceilings, internal and external plastering, putting a plastic membrane under the floor, and sealing the foundation of the house.
Water conservation methods: 15% of the fresh water supplies in the world are used by buildings. Buildings will use less water as a result of installing ultra-low flow fixtures, rain-water recovery systems, updating outdated plumbing, and other cutting-edge water technology. This is due to a growing awareness of the worldwide fresh water supply situation.
Living walls or Vertical Garden: With or without the use of soil, living walls, bio walls, or vertical gardens can be grown on nearly any kind of wall and can be installed both inside and outside. A popular example of a living wall is at the Museeduquai Branly in Paris, there is a well-known illustration of a living wall. These walls make an effort to draw air via the wall’s root system using photo remediation and bio-filtration. active microorganisms that are beneficial.
Green Concrete: An eco-friendly concrete is green concrete. The three pillars of sustainability—environmental, economic, and social impacts—are all improved by using green concrete. Reduce, reuse, and recycle principles, or any two con Crete technology procedures, should be followed for producing green concrete. Reduced greenhouse gas emissions, reduced use of natural resources like limestone, shale, clay, natural river sand, and natural rocks that are consumed for human development but not returned to the earth, and reduced use of waste materials in concrete that contribute to air, land, and water pollution are the three main goals of the green concept in concrete. This goal of “green concrete” will lead to sustainable development without depletion of the environment’s resources.
Conclusion: The uptake of green building concepts and techniques is largely focused on eco-efficiency and healthy living. So, with new technologies constantly being developed to complement current practices in creating green structures, by adopting greener practices, we can take maximum advantage of environmental and economic performance. To live a healthy life, we should concentrate on green building aspects.
Reference:
- Dibas Manna, Sulagno Banerjee (2019): A Review on Green Building Movement in India: International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research, Volume 8, Issue 10, ISSN 2277-8616.
- Yingling Shi and Xinping Liu (2019): Research on the Literature of Green Building Based on the Web of Science: A Scient metric Analysis in Cite Space (2002–2018). Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute (MDPI), volume 11.
- Apoorva V. Kotkar, Prof. Hemant Salunkhe (2017): International Journal of Advance Research in Science &Engineering, Volume 6, Issue 7,ISSN 2319-8354.
- Sumateja Reddy (2016); The Emerging Trends in Green Building Construction Practice. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, Volume 7, Issue 10, ISSN 2229-5518.
- Indoor Air Facts No.4 (revised) Sick building syndrome. Available from: http:/www.epa.gov/iaq/pubs/sbs.